Understanding Diabetes: Causes, Complications, and Management
Did you know that nearly 50 million new cases of diabetes are reported worldwide every year? While it may seem like a condition that mostly affects older adults, diabetes can impact anyone. Despite its prevalence, many people still do not fully understand this disease. This article explains the basics of diabetes, its causes, potential complications, and effective management strategies.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition where the body either does not produce enough insulin, cannot use insulin effectively, or develops insulin resistance. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels by helping cells absorb glucose for energy. When glucose builds up in the bloodstream instead of being used by the body, insulin is released to manage it.
Type 1 Diabetes occurs when the immune system destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, resulting in little or no insulin production. Type 2 Diabetes happens when the pancreas still produces insulin, but the body does not respond properly, leading to high blood sugar levels. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for carbohydrates is 55-70 grams during fasting and 56-84 grams when not fasting.
[Read More: Molecular Pathology]Causes and Risk Factors of Diabetes
Several factors can increase the risk of developing diabetes:
- Obesity: Excess body fat can alter hormone levels, increasing appetite and weight gain, which is linked to type 2 diabetes.
- Genetics: A family history of diabetes can increase your risk.
- Age: The likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes rises with age.
- Race and Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups are more prone to type 2 diabetes.
- Lifestyle and Environment: Poor diet, lack of exercise, and unhealthy habits significantly contribute to diabetes risk.
Complications of Diabetes
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious health issues:
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Common in type 1 diabetes, this condition occurs when ketone levels rise dangerously, potentially causing coma or death.
- Neuropathy: Prolonged high blood sugar can damage nerves in the hands, feet, and other areas, causing numbness, tingling, or pain.
- Eye Problems: High blood sugar can damage the eyes, resulting in diabetic retinopathy or macular edema, which can lead to vision loss.
- Kidney Damage: Excess blood sugar increases urine production and puts stress on the kidneys, raising the risk of kidney disease.
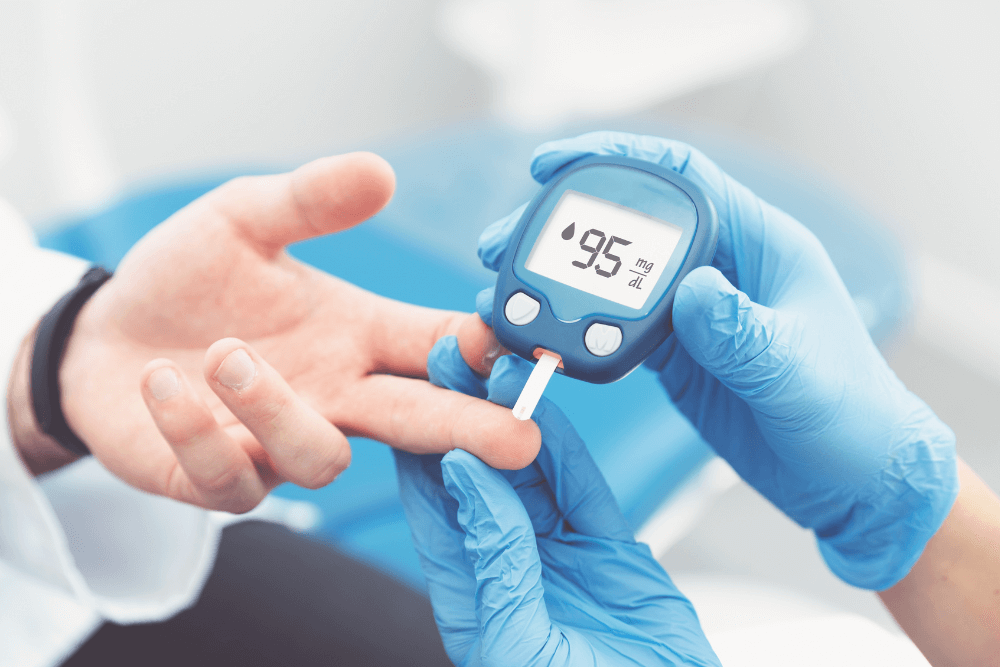
How to Control Diabetes
Effective diabetes management requires early intervention and consistent care:
- Monitor Blood Sugar: Regular testing is essential for keeping diabetes under control.
- Maintain Healthy Blood Pressure: High blood pressure increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Control Cholesterol: Balanced cholesterol levels protect heart health.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reducing excess body fat lowers diabetes risk and improves overall health.
- Manage Triglycerides: Keeping triglyceride levels in check helps prevent cardiovascular complications.
- Follow Medication Guidelines: Always take prescribed medications as directed and consult a doctor before making any changes.
Diabetes-Friendly Diet
A well-balanced diet is crucial for controlling blood sugar and preventing complications. Focus on nutrient-rich foods and proper calorie intake:
- Protein: Supports blood sugar control and prevents muscle breakdown. Choose lean options like poultry, fish, eggs, and low-fat dairy.
- Carbohydrates: Complex carbs like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are better for blood sugar regulation than refined carbs.
- Healthy Fats: Include fats from fish, nuts, seeds, and plant oils to promote heart health.
- Hydration: Drink at least six glasses of water daily to stay hydrated and support metabolism.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes effectively requires regular monitoring, a balanced diet, and consistent exercise. Keeping your blood sugar levels close to normal can prevent complications and help you maintain a healthy, active lifestyle.










